VHR example
Contents
VHR example#
Let’s use EOReader with Very High Resolution data.
Imports#
import os
import logging
# EOReader
from eoreader.reader import Reader
from eoreader.bands import GREEN, NDVI, TIR_1, CLOUDS, HILLSHADE, to_str
from eoreader.env_vars import DEM_PATH
Create the logger#
# Create logger
logger = logging.getLogger("eoreader")
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
# create console handler and set level to debug
ch = logging.StreamHandler()
ch.setLevel(logging.INFO)
# create formatter
formatter = logging.Formatter('%(message)s')
# add formatter to ch
ch.setFormatter(formatter)
# add ch to logger
logger.addHandler(ch)
Open the VHR product#
Please be aware that EOReader will always work in UTM projection.
So if you give WGS84 data, EOReader will reproject the stacks and this can be time-consuming
# Set a DEM
os.environ[DEM_PATH] = os.path.join(
"/home", "data", "DS2", "BASES_DE_DONNEES", "GLOBAL",
"MERIT_Hydrologically_Adjusted_Elevations", "MERIT_DEM.vrt"
)
# Open your product
path = os.path.join("/home", "data", "DATA", "PRODS", "PLEIADES", "5547047101", "IMG_PHR1A_PMS_001")
reader = Reader()
prod = reader.open(path, remove_tmp=True)
prod
eoreader.PldProduct 'PHR1A_PMS_202005110231585_ORT_5547047101'
Attributes:
condensed_name: 20200511T023158_PLD_ORT_PMS_5547047101
path: /home/data/DATA/PRODS/PLEIADES/5547047101/IMG_PHR1A_PMS_001
constellation: Pleiades
sensor type: Optical
product type: Ortho Single Image
default resolution: 0.5
acquisition datetime: 2020-05-11T02:31:58
band mapping:
BLUE: 3
GREEN: 2
RED: 1
NIR: 4
NARROW_NIR: 4
needs extraction: False
cloud cover: 0.0
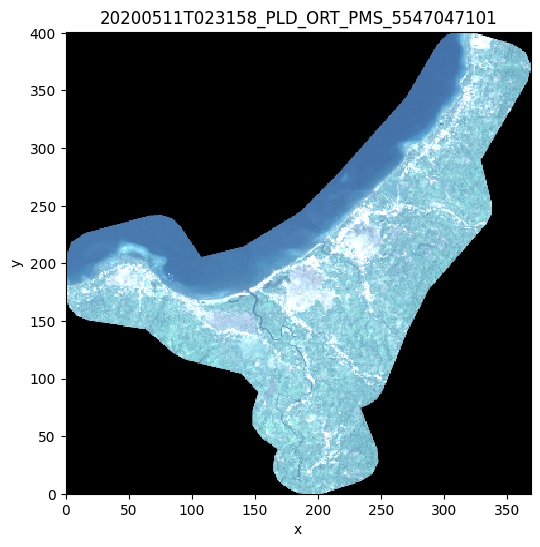
# Plot the quicklook
prod.plot()
/opt/conda/lib/python3.10/site-packages/rasterio/__init__.py:277: NotGeoreferencedWarning: Dataset has no geotransform, gcps, or rpcs. The identity matrix will be returned.
dataset = DatasetReader(path, driver=driver, sharing=sharing, **kwargs)
/opt/conda/lib/python3.10/site-packages/rioxarray/_io.py:924: NotGeoreferencedWarning: Dataset has no geotransform, gcps, or rpcs. The identity matrix will be returned.
warnings.warn(str(rio_warning.message), type(rio_warning.message)) # type: ignore
# Get the bands information
prod.bands
eoreader.SpectralBand 'RED'
Attributes:
id: 1
eoreader_name: RED
common_name: red
gsd (m): 0.5
asset_role: reflectance
Center wavelength (nm): 650.0
Bandwidth (nm): 120.0
eoreader.SpectralBand 'GREEN'
Attributes:
id: 2
eoreader_name: GREEN
common_name: green
gsd (m): 0.5
asset_role: reflectance
Center wavelength (nm): 560.0
Bandwidth (nm): 120.0
eoreader.SpectralBand 'BLUE'
Attributes:
id: 3
eoreader_name: BLUE
common_name: blue
gsd (m): 0.5
asset_role: reflectance
Center wavelength (nm): 495.0
Bandwidth (nm): 70.0
eoreader.SpectralBand 'NIR'
Attributes:
id: 4
eoreader_name: NIR
common_name: nir
gsd (m): 0.5
asset_role: reflectance
Center wavelength (nm): 840.0
Bandwidth (nm): 200.0
eoreader.SpectralBand 'NIR'
Attributes:
id: 4
eoreader_name: NIR
common_name: nir
gsd (m): 0.5
asset_role: reflectance
Center wavelength (nm): 840.0
Bandwidth (nm): 200.0
print(f"Acquisition datetime: {prod.datetime}")
print(f"Condensed name: {prod.condensed_name}")
Acquisition datetime: 2020-05-11 02:31:58
Condensed name: 20200511T023158_PLD_ORT_PMS_5547047101
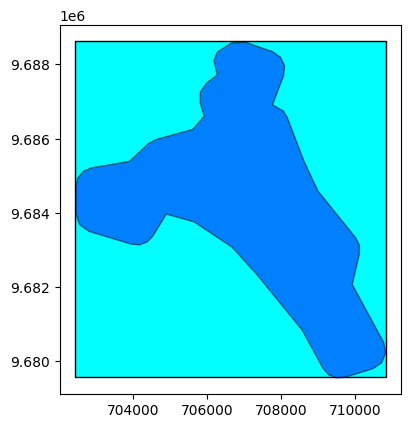
# Open here some more interesting geographical data: extent and footprint
extent = prod.extent()
footprint = prod.footprint()
base = extent.plot(color='cyan', edgecolor='black')
footprint.plot(ax=base, color='blue', edgecolor='black', alpha=0.5)
<AxesSubplot: >
Here, if you want to orthorectify or pansharpen your data manually, you can set your stack here.
prod.ortho_stack = "/path/to/ortho_stack.tif"
If you do not provide this stack, but you give a non-orthorectified product to EOReader
(i.e. SEN or PRJ products for Pleiades), you must provide a DEM to orthorectify correctly the data.
⚠⚠⚠ DIMAP SEN products are orthorectified using RPCs and not the rigorous sensor model. A shift of several meters can occur. Please refer to this issue.
Load some bands#
# Select the bands you want to load
bands = [GREEN, NDVI, TIR_1, CLOUDS, HILLSHADE]
# Be sure they exist for Pleiades sensor
ok_bands = [band for band in bands if prod.has_band(band)]
print(to_str(ok_bands)) # Pleiades doesn't provide TIR and SHADOWS bands
['GREEN', 'NDVI', 'CLOUDS', 'HILLSHADE']
# Load those bands as a dict of xarray.DataArray
band_dict = prod.load(ok_bands)
band_dict[GREEN]
Reprojecting band NIR to UTM with a 0.5 m resolution.
Reprojecting band RED to UTM with a 0.5 m resolution.
Reprojecting band GREEN to UTM with a 0.5 m resolution.
<xarray.DataArray 'GREEN' (band: 1, y: 18124, x: 16754)>
array([[[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
...,
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[nan, nan, nan, ..., nan, nan, nan]]], dtype=float32)
Coordinates:
* band (band) int64 1
* x (x) float64 7.024e+05 7.024e+05 ... 7.108e+05 7.108e+05
* y (y) float64 9.689e+06 9.689e+06 9.689e+06 ... 9.68e+06 9.68e+06
spatial_ref int64 0
Attributes:
cleaning_method: nodata
long_name: GREEN
constellation: Pleiades
constellation_id: PLD
product_path: /home/data/DATA/PRODS/PLEIADES/5547047101/IMG_PHR1A_PM...
product_name: PHR1A_PMS_202005110231585_ORT_5547047101
product_filename: IMG_PHR1A_PMS_001
instrument: HiRI
product_type: Ortho Single Image
acquisition_date: 20200511T023158
condensed_name: 20200511T023158_PLD_ORT_PMS_5547047101
orbit_direction: DESCENDING
radiometry: reflectance
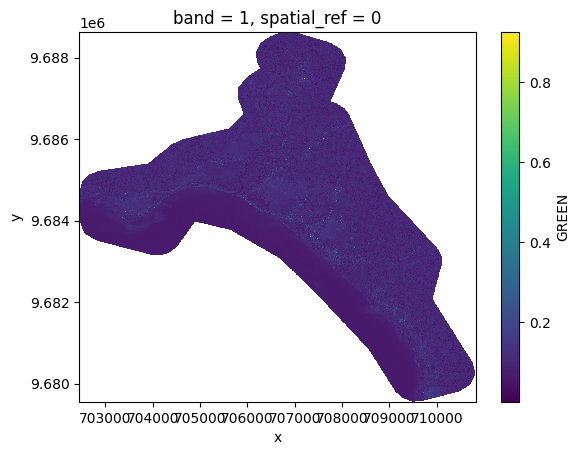
cloud_cover: 0.0# The nan corresponds to the nodata you see on the footprint
# Plot a subsampled version
band_dict[GREEN][:, ::10, ::10].plot()
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f2813e41ed0>
# Plot a subsampled version
band_dict[NDVI][:, ::10, ::10].plot()
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f2810177d00>
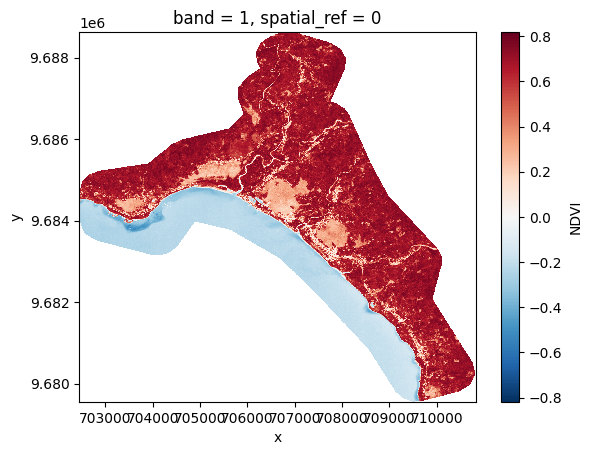
# Plot a subsampled version
band_dict[CLOUDS][:, ::10, ::10].plot()
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f281007d450>
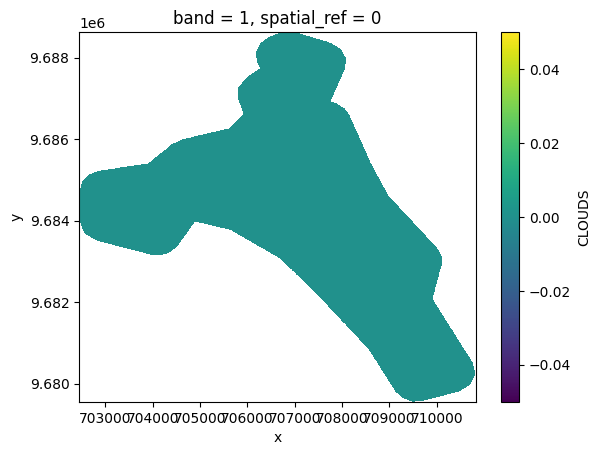
# Plot a subsampled version
band_dict[HILLSHADE][:, ::10, ::10].plot()
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f28100f1bd0>
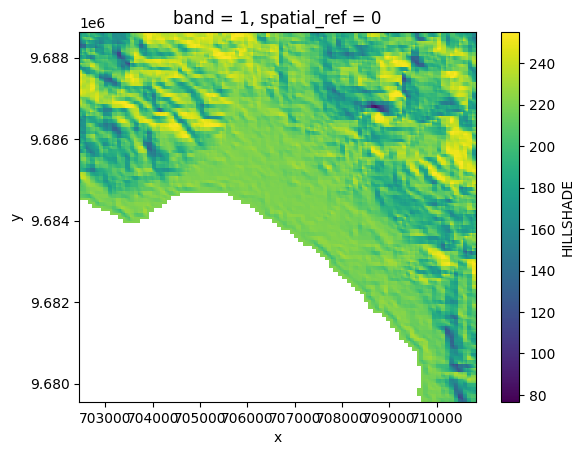
Stack some bands#
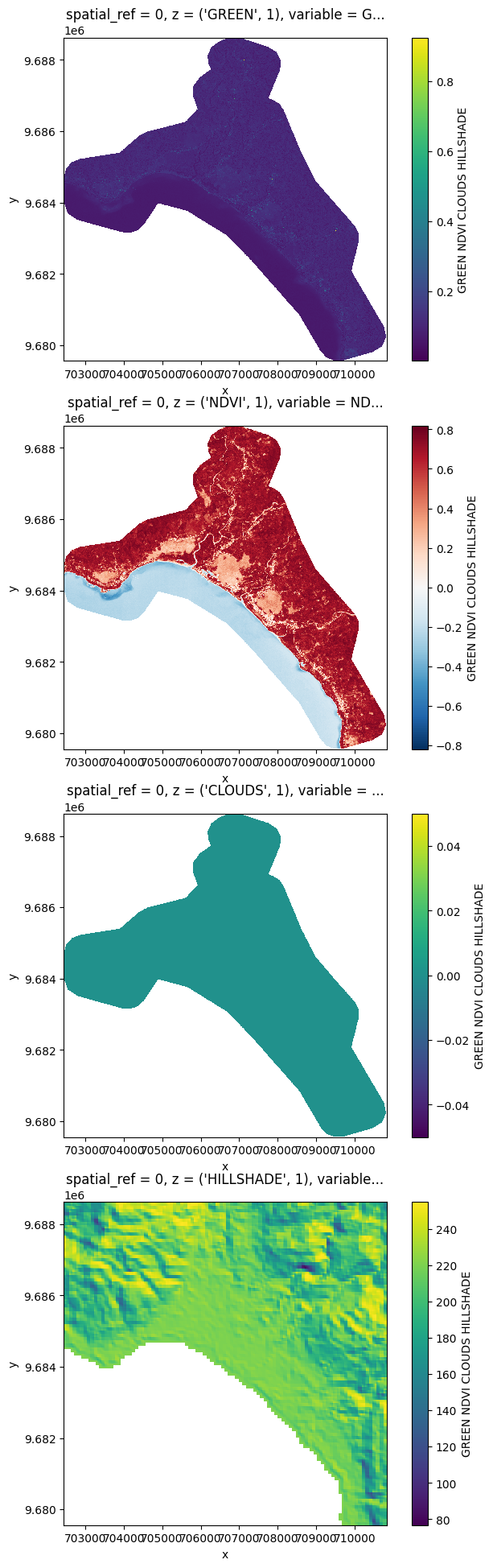
# You can also stack those bands
stack = prod.stack(ok_bands)
# Plot a subsampled version
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
nrows = len(stack)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=nrows, figsize=(2 * nrows, 6 * nrows), subplot_kw={"box_aspect": 1})
for i in range(nrows):
stack[i, ::10, ::10].plot(x="x", y="y", ax=axes[i])